Denitrification, SNCR systems
With the selective non-catalytic reaction (SNCR), nitrogen oxides (Nox), which are produced in all industrial combustion processes, can be reliably removed from the exhaust gas. Our many years of expertise in the field of process and control engineering helps us to optimally design the SNCR process for your plant. design and more more than
80 % of the NOx-emissions from the exhaust gas. This allows legal NOx-limits are reliably adhered towhich an important contribution for to our environment.
Dhe SNCR method represents is a cost-effective solution that can be easily integrated into existing systems. The investment costs for the SNCR process are only approx. 10-20 % of the costs of an SCR process. of an SCR process. We also analyze and optimize existing SNCR systems and support you in the saving of reducing agents (urea/ammonia)in order to the operating costsminimize operating costs.
Our goal is to the technically and economically best possible solution for your plant to meet the current and future NOx-emission limits with minimum consumption of reducing agent reliably.
Would you like to find out more? Should we call you or would you like to receive further information by e-mail?
I am happy to be there for you!
The advantages of the SNCRprocedure at a glance:
- High efficiency (more than 80 % NOx capture efficiency possible)
- Low investment costs (up to 10 times lower than an SCR–process)
- Low operating costs (no additional pressure loss in the exhaust gas flow, no reheating of the exhaust gas necessary)
- Quick and easy to retrofit to existing systems
- Less space required compared to the SCR–process
Our services in detail:
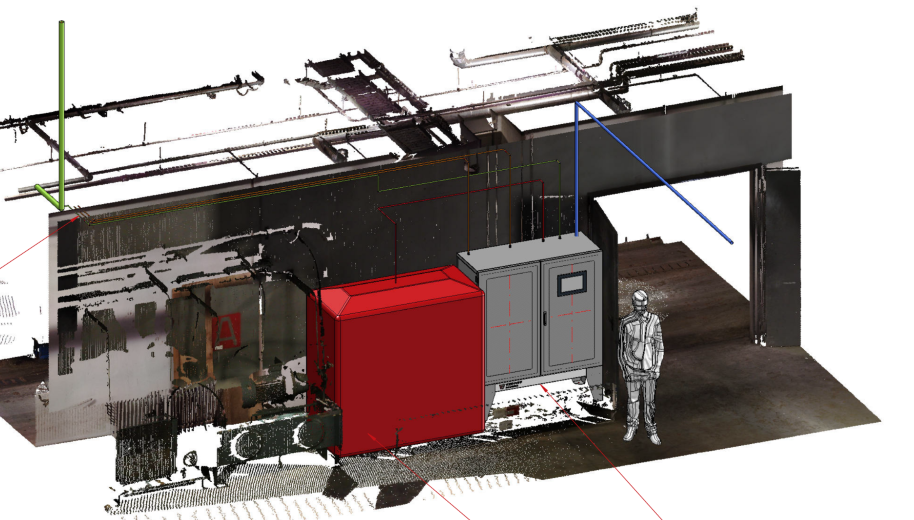
We come and analyze your circumstances – existing plant technology, process parameters and the space available at the site – simply all the requirements and framework conditions to create the best possible technical and economic concept for NOx reduction. The result of the conception phase is a resilient concept for your custom-fit SNCR – clear in terms of technical, economic and scheduling aspects, as a decision-making basis for implementation.
Our services in the concept phase are
-
Combustion analysis (grate furnaces, rotary kilns, fluidized bed systems)
-
Determining the consumption of operating resources
-
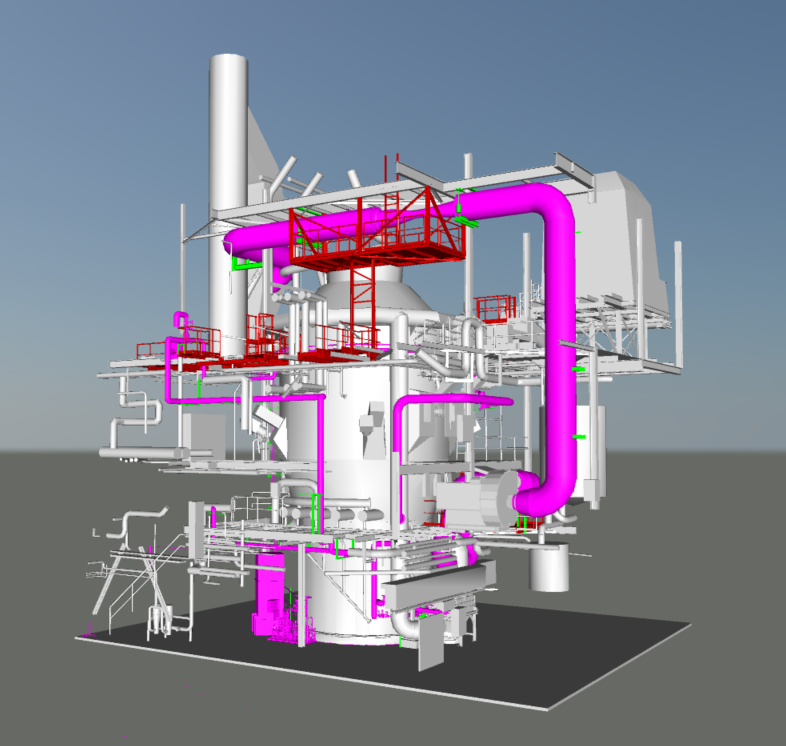
Process flow diagram and process description
-
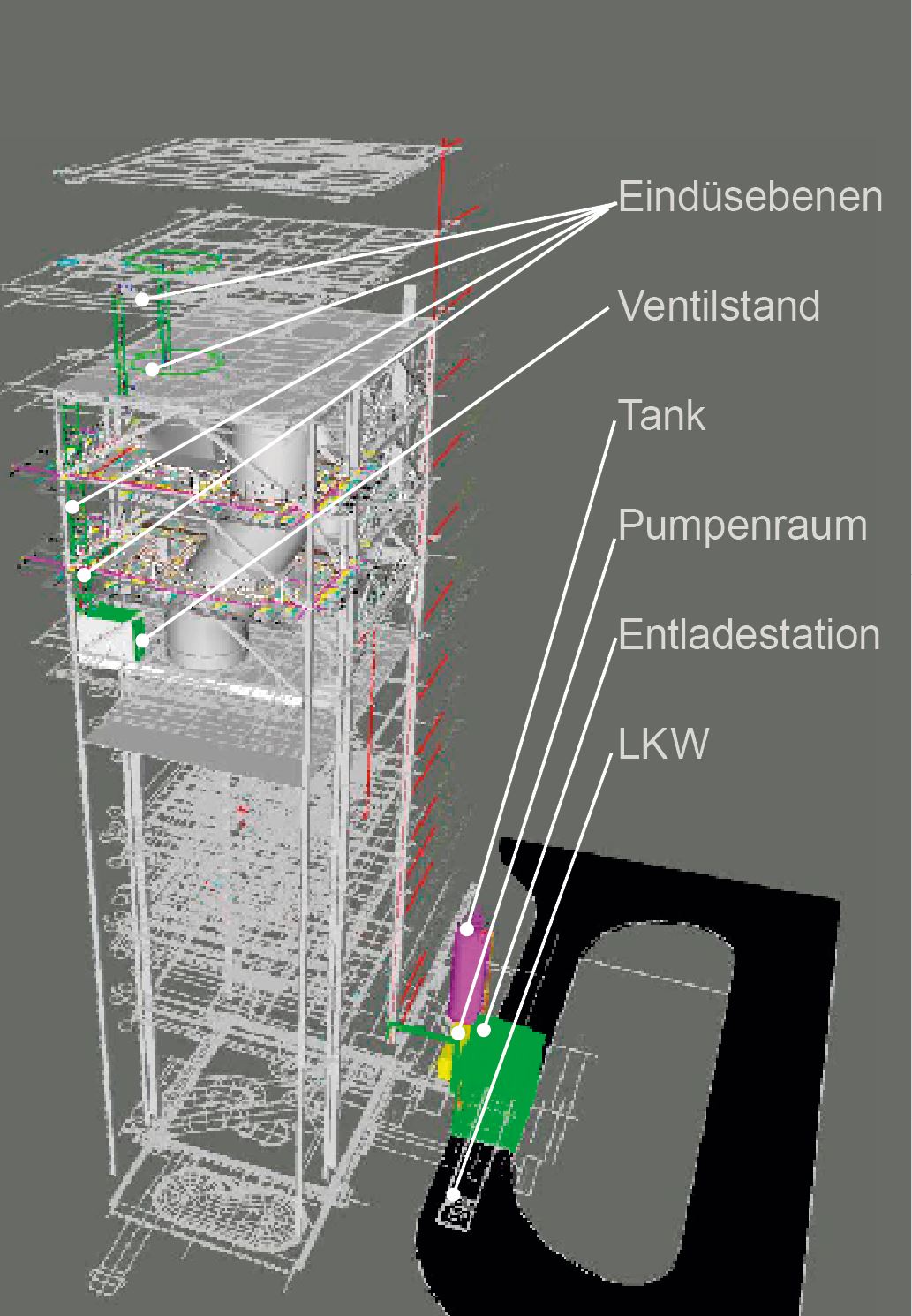
Specification of the main components (nozzles, pumps, fittings,…) and interfaces to other trades
-
Rough estimate of the investment costs
.
Based on the developed concept, we accompany you through the engineering phases of the project, such as basic engineering and detail engineering, and also support you afterwards in the execution of the project. We tailor our services to your needs, saving you time and money.
In the basic engineering phase, the technical solution developed in the concept phase is further specified and investment costs and possible risks are evaluated. In the detailed engineering phase, the focus is on the preparation of documents ready for implementation, which are required for the procurement and construction of the system as well as its commissioning and further operation.
Our engineering services are:
-
Creation of process flow diagrams and PIDs
-
Process and function description
-
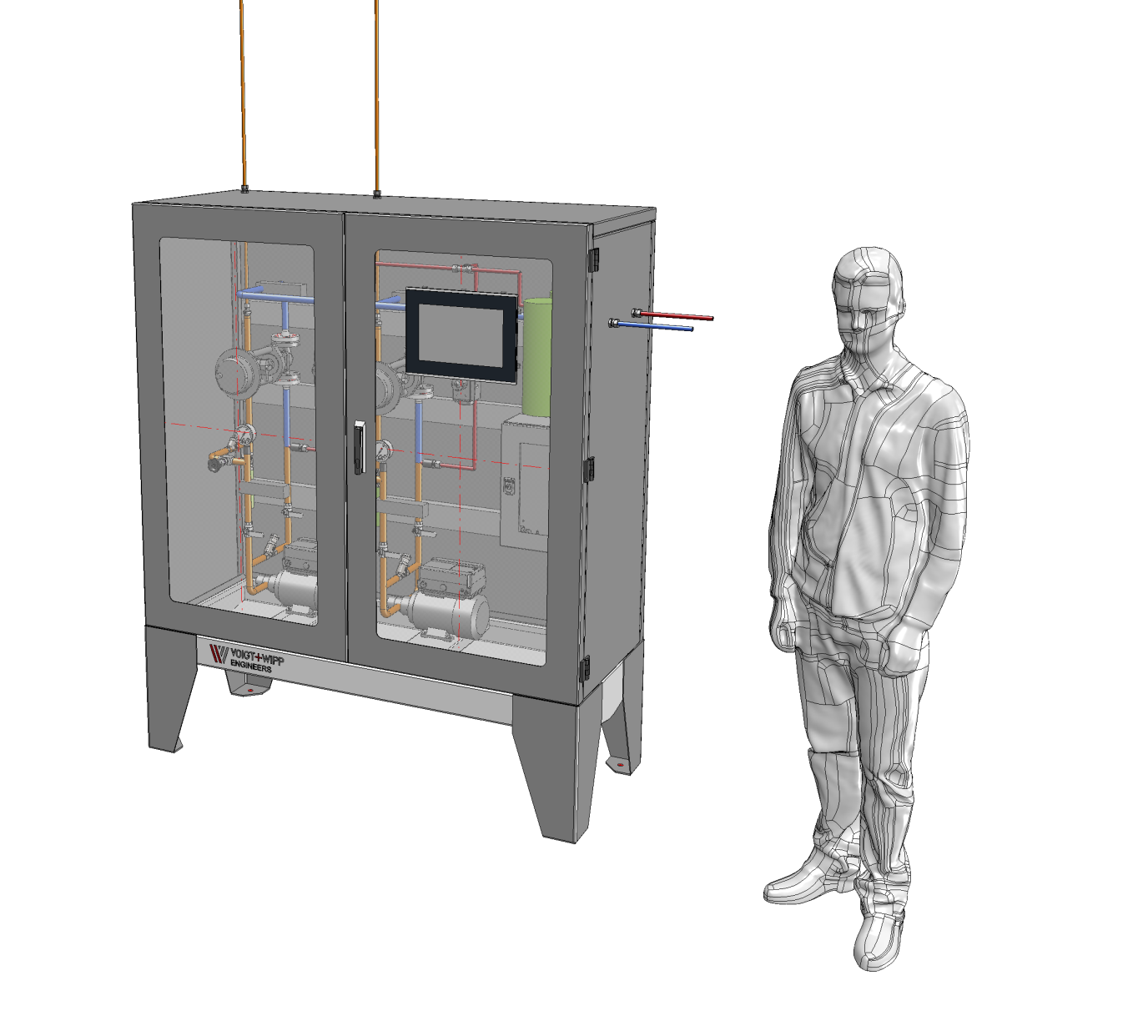
Component and MSR lists (complete specification of the components)
-
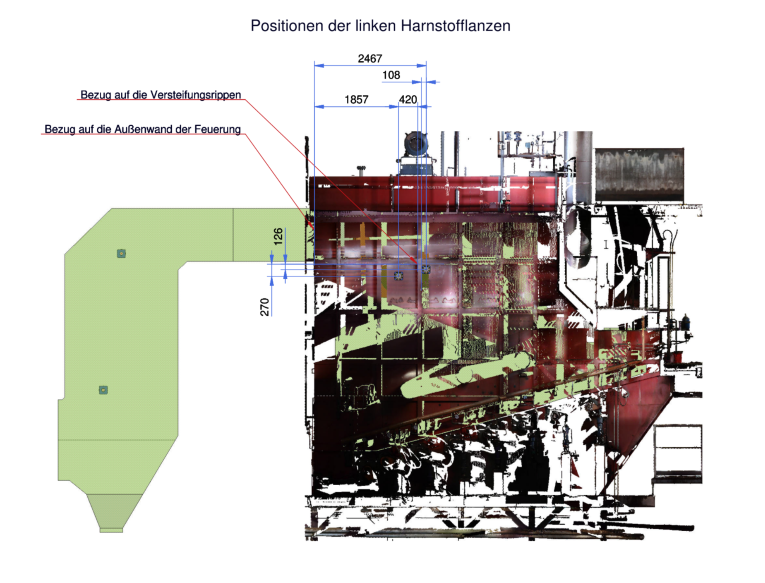
3D laser scan for measurement
-
Detailed 3D planning (installation planning, pipe planning, steel construction, etc.)
-
Support with system approval (communication with authorities, compilation of required documents)
-
Risk assessment (HAZOP)
From engineering, procurement and delivery to installation and commissioning, the CONENGA Group provides you with everything from a single source.
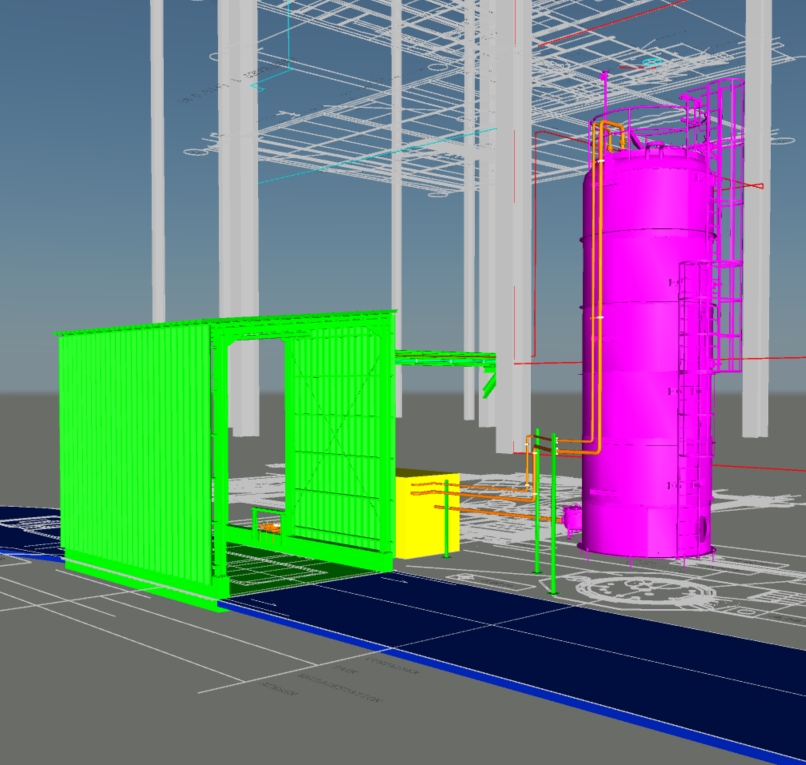
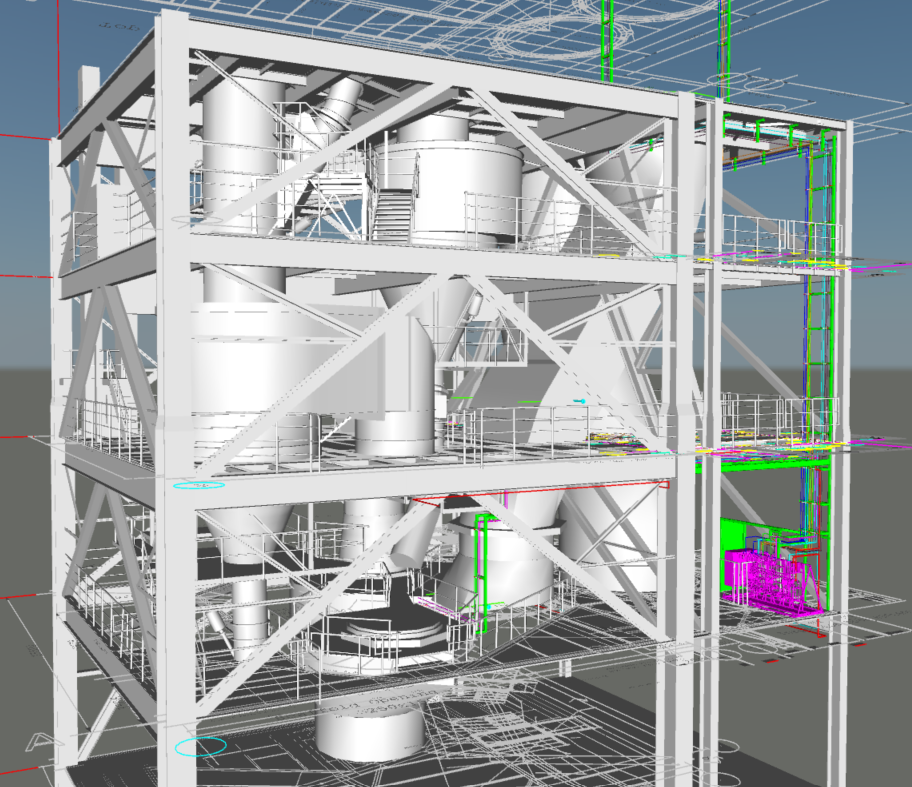
Thanks to our many years of experience components, from the pump stand to the nozzle, are optimally matched to each other and guarantee high availability, optimum cost-effectiveness and trouble-free, efficient operation. We adapt our specially developed and proven APC technologies for our SNCR control system to the specific requirements with regard to the required separation efficiency and number of lance levels in order to offer you the best possible cost-benefit ratio. Stable and low-fluctuation NOx emission control and the avoidance of overdosing the reducing agent can reduce reducing agent consumption and minimize ongoing operating costs. The SNCR system we have developed is also characterized by simple and intuitive operation and a high degree of automation.
Your benefit:
-
Complete SNCR system at an all-inclusive price incl.
-
-
Engineering, procurement, installation and commissioning from a single source
-
-
-
Support with official procedures
-
-
-
CE marking for the overall performance delivered
-
-
-
Continuous project management from the concept phase to final acceptance
-
-
Minimal use of reducing agents thanks to consumption-optimized, intelligent control
-
High system availability thanks to the use of high-quality components
-
Easy operation of the system and low maintenance requirements thanks to a high degree of automation
-
Lower risk due to fewer interfaces
We support your interest in the economical operation and long-term value retention of your SNCR system and are available to you as a service partner throughout its service life.
Coordinated with your own capacities, we support you in maintaining optimum operation. This is based on the service and maintenance plan for SNCR, which is included as a performance part. Thanks to the secure digital connection ongoing optimization, adaptation to changing conditions, changes in fuel or plant can be made. Reducing agent consumption is continuously kept at the lowest possible level, and changes are detected at an early stage.
We contribute our extensive know-how on combustion technologies (grate firing, fluidized bed, rotary kiln) and the corresponding process engineering. Your plant remains “state of the art”.
Customer testimonial:
“As part of the upgrade of our fluidized bed boiler by the experts from VOIGT+WIPP Engineers, an SNCR system was also integrated. This not only enables the emission limits to be undercut, it also proves to be stable and reliable in operation after more than a year of use. The SNCR control system was implemented as part of the integrated EPOC suite.”
DI (FH) Bernhard Pichler, Project Manager, NORSKE SKOG